Walking, yoga, and strength training are all suggested to be beneficial treatments for depression, according to a British Medical Journal study.
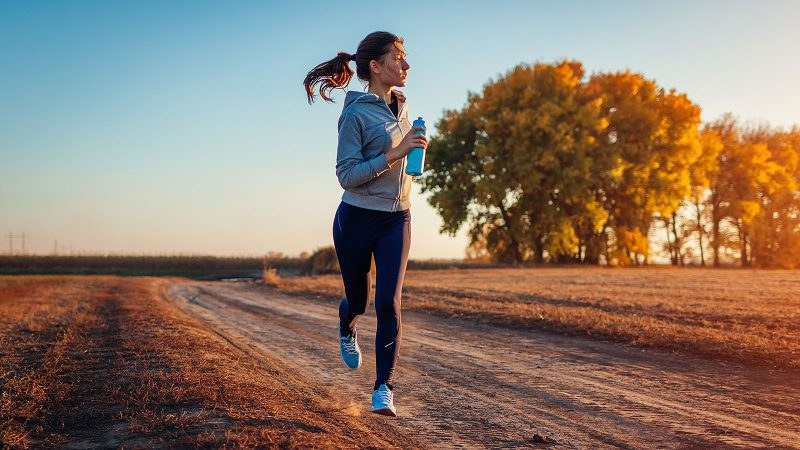
As to a British Medical Journal study, depression can be effectively treated with yoga, strength training, and walking/jogging. The study discovered that while low-intensity exercise is beneficial, higher-intensity exercise typically had even more advantages. According to the World Health Organization, 300 million people worldwide suffer from depression. According to the paper, major depressive disorder is the leading cause of disability globally and has been shown to have a greater negative impact on life satisfaction than diabetes, debt, and divorce.
Exercise has been suggested as one of the “core treatments” for depression, along with psychotherapy and medication, however rules for the most effective way to prescribe exercise for depression remain unclear. The investigators examined 218 pertinent studies with 14,170 depressed patients. Exercise type, intensity, and frequency were noted, and each trial’s bias was evaluated.
It was discovered that jogging or walking works well for both men and women. Strength training was most beneficial for younger persons and women, whereas yoga proved more beneficial for males and older folks.
Juan Ángel Bellón from the University of Malaga noted in a linked editorial that individuals with depression may find it difficult to exercise regularly because they frequently exhibit signs of exhaustion and poor vitality. “should provide enough resources to make individualised and supervised exercise programmes accessible to the entire population,” the author stated.
The BMJ study’s authors note that there is a dearth of research tracking individuals for a year or more, and the quality of the data is poor. It was also mentioned that a lot of patients can have social, psychological, or physical obstacles to participation.
The World Health Organization estimates that 300 million people worldwide suffer from depression. Exercise is often recommended in addition to psychotherapy and medicine, yet the best technique to prescribe exercise for depression remains a topic of debate among treatment guidelines and previous data assessments.